Cognitive Dual-Process Theories Applied to Artificial Intelligence
Teorías Cognitivas de Procesamiento Dual aplicadas a la Inteligencia Artificial
Barra lateral del artículo
Términos de la licencia (VER)

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-SinDerivadas 4.0.
Declaración del copyright
Los autores ceden en exclusiva a la Universidad EIA, con facultad de cesión a terceros, todos los derechos de explotación que deriven de los trabajos que sean aceptados para su publicación en la Revista EIA, así como en cualquier producto derivados de la misma y, en particular, los de reproducción, distribución, comunicación pública (incluida la puesta a disposición interactiva) y transformación (incluidas la adaptación, la modificación y, en su caso, la traducción), para todas las modalidades de explotación (a título enunciativo y no limitativo: en formato papel, electrónico, on-line, soporte informático o audiovisual, así como en cualquier otro formato, incluso con finalidad promocional o publicitaria y/o para la realización de productos derivados), para un ámbito territorial mundial y para toda la duración legal de los derechos prevista en el vigente texto difundido de la Ley de Propiedad Intelectual. Esta cesión la realizarán los autores sin derecho a ningún tipo de remuneración o indemnización.
La autorización conferida a la Revista EIA estará vigente a partir de la fecha en que se incluye en el volumen y número respectivo en el Sistema Open Journal Systems de la Revista EIA, así como en las diferentes bases e índices de datos en que se encuentra indexada la publicación.
Todos los contenidos de la Revista EIA, están publicados bajo la Licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-NoDerivativa 4.0 Internacional
Licencia
![]()
Esta obra está bajo una Licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-NoDerivativa 4.0 Internacional
Contenido principal del artículo
Resumen
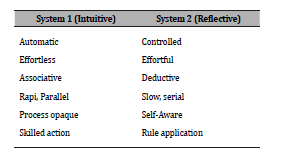
In his 2011 book Thinking, Fast and Slow, Daniel Kahneman popularized the dual-process theory of cognition through the distinction between System 1—fast, automatic, and associative—and System 2—slow, deliberate, and rule-based. His research, which integrates economic theory with cognitive psychology, revealed the pervasiveness of cognitive biases and showed how the interaction between these systems can systematically lead to reasoning errors.
This article explores the applicability of Kahneman’s dual-process framework to artificial learning systems, particularly in addressing phenomena such as hallucinations and inference failures in large language models. We examine the cognitive mechanisms involved in idea formation at the neural level and propose two postulates that outline the structural challenges in implementing a System 2 analogue in artificial intelligence.
Given that machine learning systems rely on mathematical formalisms, we introduce a simplified mathematical model of cognitive processing. This model suggests that an axiomatic understanding of synaptic behaviour may be crucial to identifying and mitigating systematic reasoning flaws in natural language processing systems.
Descargas
Detalles del artículo
Referencias (VER)
Anil, R., Andrew, M. D., Orhan, F., Melvin, J., Dmitry, L., Alexandre, P., . . . al., e. (20223). Palm 2 technical report. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.10403.
Chowdhary, K. (2020). Fundamentals of artificial intelligence. Springer.
Fjelland, R. (2020). Why general artificial intelligence will not be realized. Humanities and Social Sciences Communications, 1-9.
Google AI. (n.d.). Retrieved from Google AI: https://ai.google/discover/palm2/
Hagendorff, T., & Wezel, K. (2020). 15 challenges for AI: or what AI (currently) can’t do. Ai & Society, 355--365.
Jungnickel, D. (2005). Graphs, networks and algorithms. Springer.
Kahneman, D. (2011). Thinking, fast and slow. New York: Farrar, Straus and Giroux.
Kaplan, J. a., Gray, S., Radford, A., Wu, J., & Amodei, D. (2020). Scaling laws for neural language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2001.08361.
Newell, A., & Simon, H. A. (1959). Report on a General Problem-Solving Program. IFIP Congress, 31.
Newell, A., & Simon, H. A. (1972). Human Problem Solving. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-hall.
OpenAI. (2023). GPT-4 Technical Report. https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.08774.
Perplexity.ai. (2022). Perplexity. Retrieved from Perplexity: https://www.perplexity.ai/
Pólya, G. (1945). How to solve it. Princeton University Press.
Sarrazola-Alzate, A. (2023). Problemas estructurales en sistemas inteligentes. Una aproximación desde el programa ChatGPT. Repositorio Institucional, Fondo Editorial EIA.
Sel, B., Al-Tawaha, A., Khattar, V., Wang, L., Jia, R., & Jin, M. (2023). Algorithm of thoughts: Enhancing exploration of ideas in large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.10379.
Shunyu, Y., Yu, D., Zhao, J., Izhak, S., Griffiths, T. C., & Narasimhan, K. (2024). Tree of thoughts: Deliberate problem solving with large language models. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems.
Wang, P. (2019). On definig artificial inteligence. Journal of Artificial General Intelligence, 1-37.
Wei, J., Wang, X., Schuurmans, D., Bosma, M., Xia, F., Chi, E., . . . others. (2022). Chain-of-thought prompting elicits reasoning in large language models. Advances in neural information processing systems, 24824-24837.
Whitehead, A. N., & Russell, B. (1927). Principia mathematica. Cambridge University Press.
Wu, T., Shizhu, H., Jingping, L., Sun, S., Kang, L., Qing-Long, H., & Yang, T. (2023). A brief overview of ChatGPT: The history, status quo and potential future development. Journal of Automatica Sinica, 1122-1136.
Yao, S., Yu, D., Zhao, J., Shafran, I., Griffiths, T., Cao, Y., & Narasimhan, K. (2024). Tree of thoughts: Deliberate problem solving with large language models. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems.
Zhang, Y., Wang, X., Wu, L., & Wang, J. (2024). Pattern-Aware Chain-of-Thought Prompting in Large Language Models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2404.14812.
Zhang, Z., Zhang, A., Li, M., & Smola, A. (2022). Automatic chain of thought prompting in large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.03493.
Zhao, Wayne, X., Kun, Z., Junyi, L., Tianyi, T., Xiaolei, W., . . . al., e. (2023). A survey of large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.18223.

 PDF
PDF
 FLIP
FLIP